Comparison to Whole Cucumber (with Peel)
Nutrition facts for cucumber without peel – Understanding the nutritional differences between peeled and whole cucumbers is crucial for making informed dietary choices. While peeling a cucumber might seem like a simple act, it significantly impacts its nutritional profile. The peel contains a considerable amount of beneficial nutrients often lost during preparation.
The following comparison highlights the key nutritional differences between peeled and whole cucumbers. This understanding allows for a more comprehensive appreciation of the nutritional benefits offered by this versatile vegetable.
Nutrient Differences Between Peeled and Whole Cucumber
Removing the cucumber peel results in a loss of several important nutrients. These nutrients contribute to the overall health benefits of consuming cucumbers. The following points detail these key differences.
- Fiber: A significant portion of cucumber’s fiber is concentrated in the peel. Peeling removes a substantial amount of this dietary fiber, which is essential for digestive health and regulating blood sugar levels.
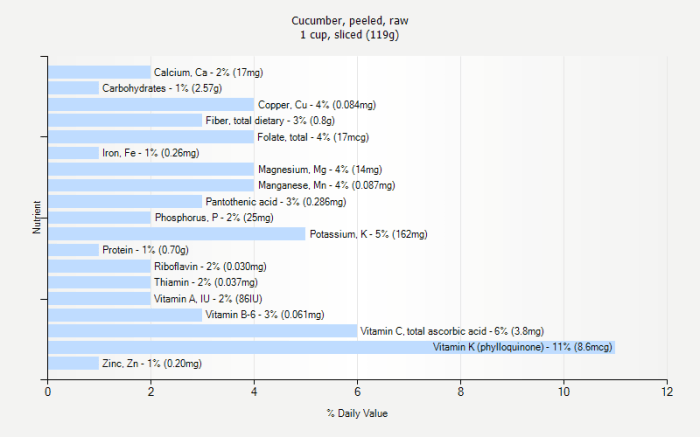
- Vitamins: The peel is a rich source of vitamins, particularly vitamin K, which is crucial for blood clotting and bone health. Other vitamins, such as vitamin C and various B vitamins, are also present in higher concentrations in the peel compared to the flesh.
- Minerals: Essential minerals like potassium, manganese, and magnesium are found in higher amounts in the cucumber peel. These minerals contribute to various bodily functions, including maintaining healthy blood pressure and supporting nerve function.
- Antioxidants: The peel contains a higher concentration of antioxidants, which help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. These antioxidants contribute to overall health and may help reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Nutritional Benefits of the Cucumber Peel, Nutrition facts for cucumber without peel
The cucumber peel offers several significant nutritional benefits often overlooked. Consuming the peel enhances the overall nutritional value of the cucumber.
- Improved Digestion: The high fiber content in the peel promotes healthy digestion and prevents constipation.
- Enhanced Nutrient Intake: As previously mentioned, the peel is a rich source of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, significantly boosting the nutritional profile of the cucumber.
- Potential Health Benefits: Some studies suggest that compounds found in cucumber peel may have anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties, although more research is needed in this area.
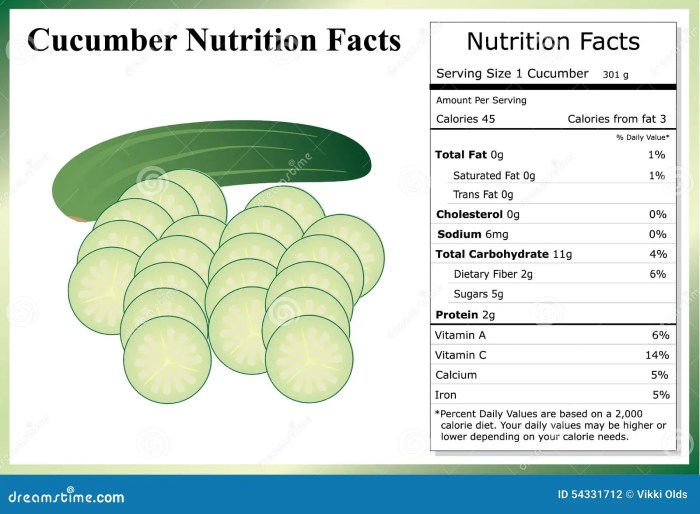
Comparison Table: Peeled vs. Whole Cucumber
The following table provides a direct comparison of the calorie count, fiber content, and vitamin C content in peeled versus whole cucumbers per 100g serving. Note that these values can vary slightly depending on the type and growing conditions of the cucumber.
| Nutrient | Peeled Cucumber (100g) | Whole Cucumber (100g) |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 12-15 | 15-18 |
| Fiber (g) | 0.5-1.0 | 1.5-2.0 |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 2-4 | 5-7 |
Cucumber in Recipes (Peeled)
Peeled cucumber, with its mild flavor and refreshing crunch, lends itself beautifully to a wide array of culinary applications. Its versatility makes it a valuable ingredient across various cuisines and dietary preferences. The absence of the peel doesn’t diminish its nutritional value significantly, offering a similar profile to the whole cucumber, but with a slightly altered texture and potentially different taste profile depending on the recipe.
Peeled cucumber’s delicate flavor profile allows it to absorb the flavors of other ingredients easily, making it an excellent base for many dishes. Its crisp texture adds a refreshing contrast to richer or heavier components.
Examples of Recipes Using Peeled Cucumber as a Primary Ingredient
The following examples illustrate the diverse ways peeled cucumber can be incorporated into delicious and nutritious meals. These recipes highlight its adaptability and its ability to complement various flavor profiles.
- Cucumber Raita: A classic Indian yogurt-based side dish featuring finely grated or diced peeled cucumber, blended with yogurt, spices like cumin and coriander, and sometimes mint or cilantro. The cool and refreshing raita balances the richness of spicier dishes.
- Gazpacho: This chilled Spanish soup often includes peeled cucumber as a key ingredient, blended with tomatoes, peppers, onions, and bread for a vibrant and flavorful summer meal. The cucumber contributes to the soup’s refreshing coolness and smooth texture.
- Cucumber Salad with Dill and Vinegar: Thinly sliced peeled cucumber tossed with fresh dill, a simple vinaigrette made with vinegar and oil, and potentially other seasonings. This salad is light, refreshing, and perfect as a side dish or a light lunch.
- Cucumber Sandwiches: Peeled cucumber, thinly sliced, makes a classic filling for sandwiches. It can be paired with cream cheese, hummus, or other spreads for a light and refreshing option.
Culinary Uses of Peeled Cucumber
Peeled cucumber’s versatility extends far beyond the examples above. Its mild flavor and refreshing texture make it a welcome addition to a variety of dishes.
While nutrition facts for cucumber without peel highlight its low calorie and high water content, a stark contrast emerges when considering the nutritional profile of other foods. For instance, checking the nilla wafers nutrition facts reveals a significantly higher sugar and fat content. This comparison underscores the importance of balanced dietary choices, highlighting how the seemingly insignificant calorie count of peeled cucumber can be overshadowed by less healthy alternatives.
- Salads: Peeled cucumber is a staple in numerous salads, adding a refreshing crunch and subtle flavor. It pairs well with tomatoes, feta cheese, olives, and various herbs.
- Dips and Spreads: Peeled cucumber can be pureed or finely diced and incorporated into dips like tzatziki (Greek yogurt dip) or other vegetable-based spreads.
- Soups and Chilis: Added to soups and chilis, peeled cucumber adds a cooling element and contributes to the overall texture.
- Drinks: Peeled cucumber can be blended into smoothies or infused into water for a refreshing beverage.
Incorporating Peeled Cucumber into Various Cuisines and Dietary Styles
Peeled cucumber’s adaptability makes it a valuable ingredient in various cuisines and dietary approaches. Its low-calorie and nutrient-rich profile makes it a perfect addition to health-conscious meals.
- Mediterranean Cuisine: Frequently used in salads, dips (like tzatziki), and as a component of mezes (appetizers).
- Indian Cuisine: A key ingredient in raitas and other side dishes, offering a refreshing contrast to spicy curries.
- Vegan and Vegetarian Diets: A versatile ingredient that can be used as a base for salads, soups, and other dishes.
- Low-Calorie Diets: Its low-calorie content makes it an ideal choice for individuals looking to manage their weight.
Preparing and Storing Peeled Cucumber
Proper preparation and storage are crucial for maintaining the freshness and nutritional value of peeled cucumber.
- Preparation: Wash the cucumber thoroughly before peeling. Peel using a vegetable peeler, ensuring even removal of the skin. Dice or slice according to the recipe’s requirements.
- Storage: Store peeled cucumber in an airtight container in the refrigerator. To maintain crispness, you can wrap it in a damp paper towel before storing. It is best consumed within a day or two of peeling to maintain its quality.
Potential Drawbacks of Removing the Peel
Removing the peel from a cucumber might seem like a simple act, but it significantly impacts its nutritional profile and can present some health-related drawbacks. The peel contains a considerable portion of the cucumber’s valuable nutrients, and consistently discarding it can lead to a less healthy diet.The peel is a rich source of dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals often lost when removed.
This loss affects not only the immediate nutritional value but also has implications for long-term health.
Nutrient Loss from Peeling
The cucumber peel is packed with vital nutrients, including vitamin K, vitamin C, and potassium. Peeling significantly reduces the intake of these essential nutrients. For instance, a substantial amount of vitamin K, crucial for blood clotting and bone health, resides in the outer layer. Similarly, removing the peel diminishes the cucumber’s potassium content, an electrolyte important for maintaining fluid balance and muscle function.
The loss of these nutrients through consistent peeling can contribute to nutritional deficiencies over time, particularly if cucumbers are a regular part of one’s diet.
Reduced Fiber Intake Due to Peeling
Dietary fiber is essential for digestive health, promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. Cucumber peel is a good source of insoluble fiber, which adds bulk to the stool and aids in digestion. By removing the peel, a considerable portion of this beneficial fiber is lost. Regular consumption of cucumbers with their peels intact contributes significantly to the recommended daily fiber intake.
A reduction in fiber intake due to consistent peeling can negatively impact gut health and lead to digestive discomfort.
Pesticide Residue and Safe Cucumber Handling
The presence of pesticide residue on the surface of cucumbers is a valid concern for many consumers. While the peel may contain higher concentrations of these residues, thorough washing is a crucial step in mitigating this risk, regardless of whether you peel the cucumber or not. Washing under running water, ideally with a vegetable brush to remove any dirt or debris, is recommended.
Choosing organically grown cucumbers can further reduce the risk of pesticide exposure. It’s important to note that while peeling might seem like a solution, it doesn’t eliminate the possibility of pesticide penetration into the flesh of the cucumber, especially if the pesticides are systemic. Therefore, a comprehensive approach of washing and potentially opting for organic produce is a more effective strategy than simply relying on peeling.
Clarifying Questions: Nutrition Facts For Cucumber Without Peel
Can I peel cucumbers that are organically grown?
While organic cucumbers generally have lower pesticide residue, peeling them still removes beneficial fiber and nutrients. Consider washing thoroughly if choosing not to peel.
Are there any specific health conditions where eating peeled cucumber is particularly beneficial or detrimental?
Individuals with digestive sensitivities might find peeled cucumber easier to digest due to reduced fiber. However, the reduced fiber could be a drawback for those aiming to increase their fiber intake. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
How long can I store peeled cucumber before it loses its nutritional value?
Peeled cucumber should be stored in an airtight container in the refrigerator and consumed within 1-2 days for optimal freshness and nutrient retention.
Does peeling a cucumber affect its taste?
Peeling can slightly alter the texture and slightly reduce the subtle bitterness some find in the peel, leading to a milder taste.
